Cloud vs, On-Premises

Ray Najem
Sales Representative & Webmaster
f these infrastructures work?
To understand how the Cloud compares to an On-premises solution, we need to first understand the infrastructure of each of them. Cloud infrastructure encompasses the various components of hardware, software, network resources, and storage systems that collectively form the backbone of cloud computing, which can be harnessed through the internet. This infrastructure is housed within extensive data centers managed by cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Whereas, the On-premises infrastructure involves physically housing all that hardware and software needed to run the IT operations locally. Having explained both infrastructures, let's weigh the strengths and weaknesses of each, so you can leverage which option makes more sense to implement.
Cloud Benefits vs. On-Premises Drawbacks
-
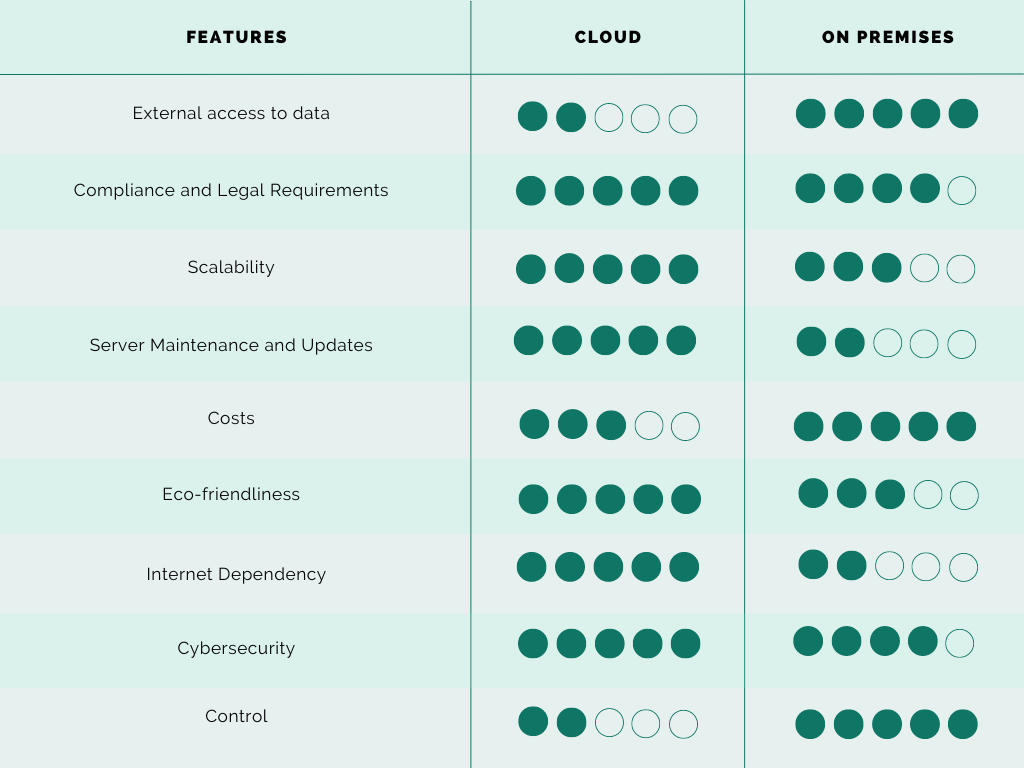
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud services allow for the instant provisioning of resources such as storage, processing power, and memory. This ease of instant scaling or even descaling can not be compared to the work to be done to scale an On-premises server. Scaling on-premises servers entail hardware upgrades such as CPU, RAM, storage, or network capacity. In addition to improving resource usage through adjustments, virtualization, or load balancing.
-
**Pay-as-you-go model: **The ability to pay for the resources that you use is a big advantage that only cloud computing offers. For businesses with a workflow that fluctuates constantly, this model offers big cost savings, as you wouldn't have to pay for the unused resources.
-
Automatic scaling features: Your cloud providers automatically adjust resources based on real time usage, so if you were to suddenly utilize more, it would be covered with no planning ahead on your end. Falling under the umbrella of agility is rapid deployment. Quick deployment of new applications and infrastructure covered by cloud services, allow for a quick, proactive approach to market demands and opportunities that may arise.
-
**Global Accessibility: **Companies looking to accommodate for the growing demand for remote work, the ability to access data and applications from whichever corner of the world you are at, is one of the biggest strengths Cloud computing has to offer. This also translates into enhanced collaboration features among team members, which is a highly sought after feature.
-
Regular Updates: Cloud service providers regularly update their services bringing you access to the latest technologies, features, security improvements ensuring you have access to the most advanced and best versions of the tool. Regularly updating the on-premises infrastructure is very time-consuming and costly, cloud computing brings the peace of mind of not having to deal with that, and instead have your cloud service provider take care.
-
Eco-Friendly: Facing climate change and human rights' challenges, a company's reputation hangs on its ethics and values. A lot of consumers now check a company's climate report, with an eye on their carbon footprint, before deciding to work with them. The main idea behind cloud computing is utilizing shared resources, which has a direct effect on energy consumption.
Weaknesses of Cloud Computing vs. On-premises Benefits
With the many advantages that cloud computing services provide, inevitably come weaknesses, which may also be where on-premises solutions shine. Here are some of those cloud weaknesses:
-
Internet dependent: Accessing the cloud relies on internet access, and how fast and reliable your internet is plays an important role on how efficiently you can work on the cloud. While cloud computing's efficiency hinges on dependable internet access, on-premises solutions stand out for their direct connectivity, all under one roof. This independence from external internet quality ensures consistent performance and access to resources, offering a stable environment for operations that demand high reliability and speed.
-
Costs: At first glance, cloud computing seems to offer a path to greater cost efficiency, especially with its flexible scaling options and lack of upfront hardware investments. However, when examining the financial implications from a long-term perspective, it becomes evident that on-premises solutions might hold the upper hand in terms of cost savings. The catch with on-premises infrastructure lies in the necessity for businesses to shoulder the burden of its management and maintenance. This includes the commitment to regular updates, security measures, and the adaptation of the system to the company's changing needs. While this path does require a more hands-on approach and potentially significant initial investments in hardware and software, the avoidance of ongoing cloud service fees, and expensive long term rental fees for the hardware utilized in the cloud can result in substantial financial benefits over the years.
-
Security concerns: This is a vital concern that many companies have when deciding which model to work with. The very nature of having your data on a server that is not under your control raises concerns; however, these are just that—mere concerns. Given the limited control one has over the cloud's actual architecture, one way to address a company's concerns is by understanding the protocols used by the cloud provider and make sure they align with the company's own security requirements. Whereas, with an On-premises solution, the company can decide for itself to implement the protocols that best align with its security requirements.
-
Limited control: As the cloud services come with pre-configured options, it might not suit all business needs. This is to say that it cannot be tailored like having an on-premises solutions which give the company direct control and customization capabilities, but that is at a cost.
-
Access to Data: An on-premises solution allows for full control of data access, eliminating the potential for unauthorized access. The cloud, by its nature of being hosted elsewhere and managed by a provider, implies that the provider can access the data since they possess the encryption keys. To mitigate this, encrypting files before uploading them is crucial. Without this security measure, files stored on cloud servers could potentially be accessible to cloud service providers. This situation highlights the importance of user-initiated encryption as a safeguard against unauthorized access, ensuring the maintenance of privacy and data integrity. However, this does not imply that cloud providers have the legal right to access your data, underscoring the significance of ISO norms and the necessity of ensuring that your provider complies with the ISO standards related to cloud services.
ISO norms to educate yourself more on the topic:
-
ISO/IEC 27017: This standard builds upon ISO 27001 and provides specific guidance for implementing information security controls for cloud services. Areas it addresses: risk assessment, service selection, contract negotiation, and ongoing monitoring for cloud environments.
-
ISO/IEC 27002: This standard provides a comprehensive list of information security controls that can be implemented within an organization, regardless of whether they use cloud services or not. These controls cover various aspects like access control, physical security, and incident management.
-
ISO 27032: This standard focuses on cybersecurity, offering guidelines for protecting information systems and assets from cyberattacks. It is applicable to both cloud and on-premises environments.
Which one is it going to be?
In concluding our exploration of cloud versus on-premises infrastructures, it's clear that each offers distinct benefits and faces unique challenges. Neither option represents a universally 'bad' choice; rather, the selection should be guided by the specific needs, strategic goals, and operational requirements of your company. As you consider your options, we encourage further education on relevant standards such as the ISO 2700x series, ISO/IEC 27017, ISO/IEC 27002, and ISO 27032. These guidelines offer valuable insights into implementing secure, effective IT infrastructures, whether in the cloud or on-premises.